|
The Camera user's interface overhaul is probably the most
significant change from introduction of the SIPS version 2.
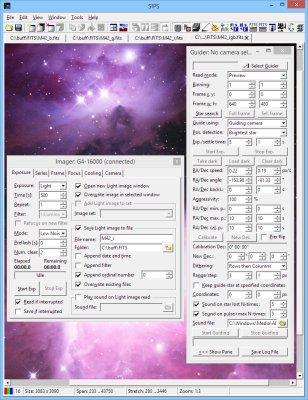
SIPS now offers separate Imaging Camera tool and Guiding
Camera tool windows Hint: New version of SIPS also contains updated documentation,
describing all new features and updates. The documentation is
accessible from the SIPS main menu Help ->
Contents... Imaging Camera tool
Changes of the Imaging Camera tool are relatively minor. Both
guiding-related tabs were removed and because there are more tools
handling more cameras, also the camera selection and configuration
is different. Instead of “interactive” tree showing current
state of all connected cameras, a modal dialog box for camera
selection was introduced (the same dialog box, but selecting
guiding camera instead of imaging camera, is used in the Guiding
Camera tool). The Camera tab of the Imaging Camera tool
shows information about the active imaging camera, beside the
camera selection button.
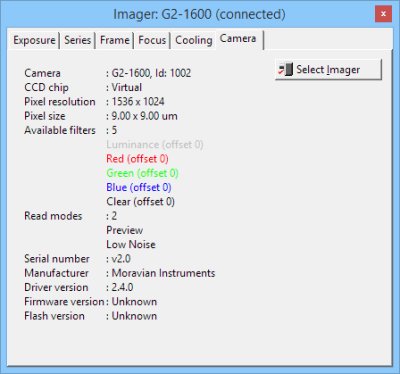
Camera tab of the Imaging Camera tool
window Another change to Imaging Camera tool is the ability to save
and load defined series of exposures.
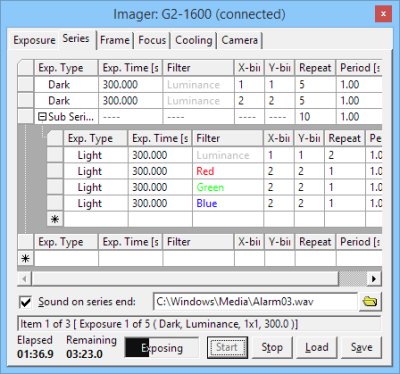
Series tab of the Imaging Camera tool
window Series description is saved into simple text file, which can be
easily edited by any text editor, providing the changes follow the
syntax rules.
SIPS Exposure Series File
list
repeat_num = 1
repeat_period = 1
item
exp_type = dark
exp_time = 3E+2
filter_index = 0
binning_x = 1
binning_y = 1
repeat_num = 5
repeat_period = 1000
end_item
item
exp_type = dark
exp_time = 3E+2
filter_index = 0
binning_x = 2
binning_y = 2
repeat_num = 5
repeat_period = 1000
end_item
list
repeat_num = 10
repeat_period = 1000
item
exp_type = light
exp_time = 3E+2
filter_index = 0
binning_x = 1
binning_y = 1
repeat_num = 2
repeat_period = 1000
end_item
item
exp_type = light
exp_time = 3E+2
filter_index = 1
binning_x = 2
binning_y = 2
repeat_num = 1
repeat_period = 1000
end_item
item
exp_type = light
exp_time = 3E+2
filter_index = 2
binning_x = 2
binning_y = 2
repeat_num = 1
repeat_period = 1000
end_item
item
exp_type = light
exp_time = 3E+2
filter_index = 3
binning_x = 2
binning_y = 2
repeat_num = 1
repeat_period = 1000
end_item
end_list
end_list
Guiding camera tool
The Guiding Camera tool user interface was programmed from the
ground up. There were two tabs covering guiding in the Camera tool
in the previous SIPS version. But these tabs somewhat artificially
divided the guiding functionality into two separate parts. They
were also full of controls and adding anything new was close to
impossible in the given area.
Images, read from the guiding camera, were handled similarly to
the images read from the main imaging camera, which could cause
some confusion (if guiding camera image has to be displayed in the
new window, it could overwrite last downloaded imaging camera
etc.). All these problems lead to new design of Guiding Camera
tool, which contains all necessary controls in the single window
as well as panes displaying guiding camera image, history charts
and log of all actions performed by the Guiding Camera tool.
Warning: Due to large number of controls and thus great
vertical size of the Guiding Camera tool window, it was necessary
to leave out some functions when SIPS runs on displays with
vertical resolution 768 or less pixels. Unfortunately this
modification caused instability of the SIPS version 2.4. Upgrade
to version 2.4.1, which fixed this problem, please. 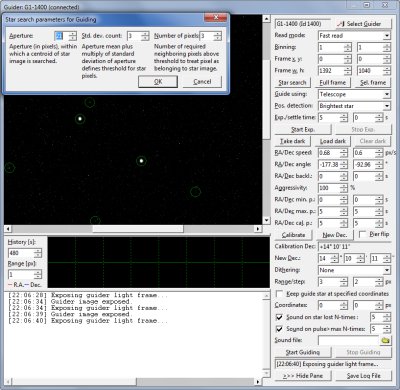
Guiding Camera tool window Because guiding is based on the ability to find star(s) on the
guiding camera image, the Guiding Camera tool helps to tune
parameters, used for star searching, by indicating of all found
stars on every read image.
Many other functions are available, like guider calibration,
altering of guiding parameters on declination change or GEM pier
swap, alarms on star lost or too long correction pulses, guiding
to fixed position or dithering while guiding. Dithering is just
opposite of fixed star position guiding. This mode is used mainly
by astrophotographers and its main purpose is to spread hot
pixels, possible bad columns and other artifacts around defined
area of the acquired images instead of keeping them on constant
position. This allows removing of artifacts during final stacking
of individual exposures by some statistical method, rejecting
extreme values (e.g. sigma clipping).
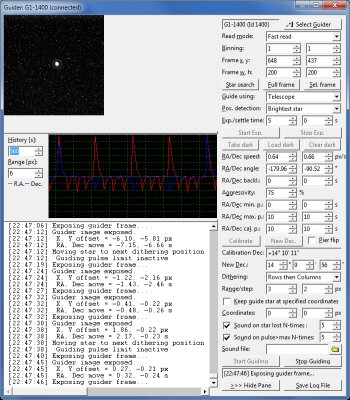
Guiding Camera tool demonstrates dithering The guiding history chart on the image above shows how
reference position is moved by 2 pixels in R.A., then a 2 pixels
shift in Dec. (move to next line) appears together with long move
in R.A. (move to beginning of the line). The main imaging camera
exposure time was set to 15 seconds only and the guiding camera
exposure time was 5 seconds for demonstration purposes only. So
the guider was able to perform only a few exposures on each offset
and the shift to next position occurred, because imaging camera
exposure finished. Such arrangement was chosen to show the shifts
on guiding chart history. In reality, imaging camera exposures are
way longer (many minutes) compared to guiding camera exposure
time.
The following image demonstrates effect of dithering.
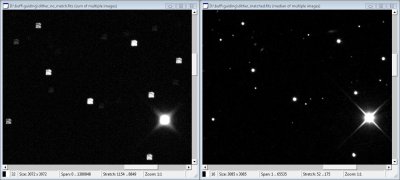
Effect of regular dithering on stacked images without
matching (left) and after matching (right) Stacking without mutual image shifts keep all hotpixels on
exactly the same position and individual stars create a grid,
which demonstrate dithering offsets. When properly stacked with
mutual matching of stars, S/N naturally significantly increases
and detector artifacts disappear.
Hint: The Guiding Camera tool has its own chapter in the SIPS
documentation. There is a guiding tutorial, explaining
calibration, regular guiding and other special functions in
detail. Other new features
Many new features, despite not as fundamental as introduction
of new Guiding Camera tool, were added to SIPS v2.4. These
enhancements include enhancements to Telescope Control tool to
control many features of the mount (e.g. the pier side control of
the German Equatorial Mounts).
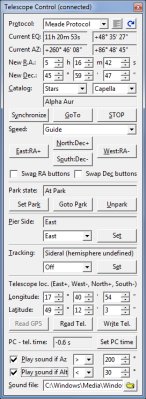
Enhanced Telescope Control tool window More small updates include keeping of the pixel under mouse
position while zooming of the image by mouse wheel (providing the
geometry of the displayed image allows it), adding the ability to
maximize zoomable tool windows (and keeping the Maximized state
between SIPS sessions), automatic identification of the Gx Camera
Ethernet Adapter within the IP network (no longer necessary to
manually enter of the adapter IP address) etc.
There is one more new tool added to SIPS—the Photometry. This is rather complex tool, maybe
the most complex one in SIPS. But the Photometry in SIPS v2.4 is
only experimental with some features not finished yet. Also the
documentation for this tool is still not ready. So take the
Photometry tool like indication of things to come.
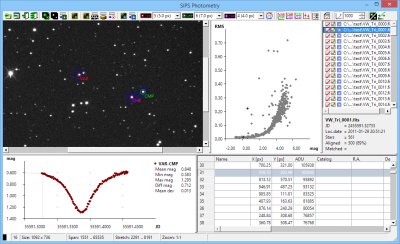
Photometry tool is still in the experimental stage in
SIPS v2.4 SIPS is a freeware and can be downloaded from the Download section of this web site.
| 