|
G4 cameras contain Full-Frame CCD chips OnSemi KAF with
37 × 37 mm detector area. These detectors
are equipped with so-called “anti-blooming gate” (ABG), which
drains the over-abundant charge from saturated pixels. ABG ensures the
round images of bright stars, without disruptive blooming spikes. On
the other side, compromising of the CCD linearity by ABG is only
negligible. G4 cameras can be used for astrometric and photometric
applications as well as ultimate camera for astrophotography.
No matter if your target is reliable scientific data or beautiful
images of deep-sky objects, G4 cameras are able to provide both.

G4-16000 camera head G4 Mark II Camera Overview
G4 camera head is designed to be easily used with a set of
accessories to fulfill various observing needs. G4 cameras do not
allow usage of internal filter wheel as they require large
50 × 50 mm filters. External filter
wheel is then the only option for G4 camera.
There are two sizes of the external filter wheel
available for the G4 cameras:
G4 camera heads are manufactured in two variants,
differing in the cooling performance:
Camera head and numerous accessories comprise imaging system,
capable to be tailored for many applications.
Components of G4 Camera system include:
G4 camera head with standard cooling G4 camera head with Enhanced Cooling (EC)
option External Filter Wheel “M” size (5 positions) External Filter Wheel “L” size (7 positions) G0 Guider camera G1 Guider camera Canon EOS bayonet adapter for Canon compatible
lenses Off-Axis Guider with M68 × 1
thread 1.75” dovetail rail for G4 camera head Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter (x86 CPU) Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter (ARM CPU) 5-positions “M” size filter wheel for 50 × 50 mm filters 7-positions “L” size filter wheel for 50 × 50 mm filters
The G4 cameras are designed to work in cooperation with
a host Personal Computer (PC). As opposite to digital still
cameras, which are operated independently on the computer, the
scientific slow-scan, cooled cameras usually require computer
for operation control, image download, processing and storage
etc. To operate the camera, you need a computer which:
Is compatible with a PC standard and runs modern 32 or
64-bit Windows operating system. Is compatible with a PC standard and runs 32 or 64-bit
Linux operating system. Support for x64 based Apple Macintosh computers is also
included.
G4 cameras require at last one free USB 2.0 port to communicate
with a host PC.
Alternatively, it is possible to use the Gx Camera Ethernet
Adapter device. This device can connect up to four Gx cameras
of any type (not only G4, but also G0, G1, G2 and G3) and offers 1
Gbps and 10/100 Mbps Ethernet interface for direct connection to
the host PC. Because the PC then uses TCP/IP protocol to
communicate with the cameras, it is possible to insert WiFi
adapter or other networking device to the communication path.
G4 Mark II Camera Models
G4 series contains the following camera models:
| Model |
CCD chip |
ABG |
Color mask |
Resolution |
Pixel size |
Image area |
Preview download |
Low-Noise download |
| G4-9000 |
KAF-09000 |
>100× |
no |
3056 × 3056 |
12 × 12 μm |
36.7 × 36.7 mm |
4.17 s |
5.77 s |
| G4-16000 |
KAF-16803 |
>100× |
no |
4096 × 4096 |
9 × 9 μm |
36.9 × 36.9 mm |
7.19 s |
10.03 s |
CCD detectors
G4 series of CCD cameras are manufactured with “Full
Frame” CCD sensors manufactured by On Semiconductor (formerly
Kodak).
CCD chip with 4096 × 4096
pixels resolution and 37 × 37 mm
area for G4-16000 camera Almost all Full Frame CCD detector area is exposed to light,
which ensures quantum efficiency provided but these sensors.
Modern FF CCD detectors are suitable also for scientific
applications, even if equipped with so-called Anti Blooming Gate
(ABG — a gate, which prohibits blooming of
the charge to neighboring pixels when image is over-exposed) with
linear enough response to light within the full dynamic range.
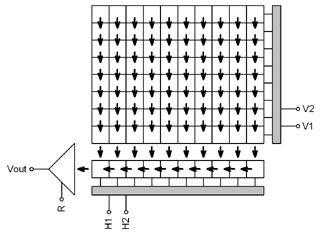
“Full Frame” CCD schematic diagram Model G4-9000
G4-9000 model uses 9 MPx OnSemi KAF-09000
Full-Frame CCD chip.
| Resolution |
3056 (H) × 3056 (V)
pixels |
| Pixel size |
12 μm (H) × 12 μm (V) |
| Image area |
36.7 mm (H) × 36.7 mm (V) |
| Full well capacity |
~110,000 e- |
| Dark current |
5 e-/s/pixel at 25 °C |
| Dark signal doubling temperature |
7 °C |
KAF-09000 CCD specifications KAF-09000 CCD and its quantum efficiency Model G4-16000
G4-16000 uses 16 MPx OnSemi KAF-16803
Full-Frame CCD chip.
| Resolution |
4096 (H) × 4096 (V)
pixels |
| Pixel size |
9 μm
(H) × 9 μm (V) |
| Image area |
36.9 mm (H) × 36.9 mm (V) |
| Full well capacity |
~100,000 e- |
| Dark current |
3 e-/s/pixel at
25 °C |
| Dark signal doubling temperature |
6.3 °C |
KAF-16803 CCD specifications KAF-16803 CCD and its quantum efficiency Camera Electronics
16-bit A/D converter with correlated double sampling ensures
high dynamic range and CCD chip-limited readout noise. Fast USB
interface ensures image download time within seconds.
Maximum length of single USB cable is approx. 5 m. This length
can be extended to 10 m or 15 m by using single USB hub or active
USB extender cable. Up to 5 hubs or active extenders can be used
in one connection.
Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter device allows connection of
up to four Gx cameras of any type through Ethernet interface and
TCP/IP network. Because TCP/IP protocol can be routed, the
distance between camera and host PC can be virtually
unlimited.
| ADC resolution |
16 bits |
| Sampling method |
Correlated double sampling |
| Read modes |
Preview mode |
| |
Low-noise mode |
| Horizontal binning |
1 to 4 pixels |
| Vertical binning |
1 to 4 pixels |
| Sub-frame readout |
Arbitrary sub-frame |
| Computer interface |
USB 2.0 High Speed |
| |
USB 1.1 Full Speed compatible |
Camera electronics specifications Image download time depends on the CCD chip used in
particular camera model. Also the read noise depends on the chip
as well as on the read mode.
Preview read mode provides system read noise
approx. 1 or 2 e- above
CCD chip read noise. Low Noise read mode is somewhat slower, but
ensures system read noise roughly equal to the
manufacturer-specified chip read noise.
Model G4-9000
| Gain |
1.5 e-/ADU (1 × 1 binning) |
| |
1.7 e-/ADU (other
binnings) |
| System read noise |
10 e- RMS (Low noise) |
| |
11 e- RMS (Preview) |
| Full frame download |
5.77 s (Low noise) |
| |
4.17 s (Preview) |
G4-9000 electronics specification Model G4-16000
| Gain |
1.6 e-/ADU (all
binnings) |
| System read noise |
11 e- RMS (Low noise) |
| |
12 e- RMS (Preview) |
| Full frame download |
10.03 s (Low noise) |
| |
7.19 s (Preview) |
G4-16000 electronics specification Notes:
Binning can be combined independently on both
axes. Stated read noise is measured on particular CCD sensor,
evaluated during camera design. Actual read noise of different
sensors varies among various manufacturing batches, but also
within single manufacturing batch. The camera read noise is
determined by the sensor itself and the camera manufacturer
cannot affect it.
Cooling and power supply
Regulated thermoelectric cooling is capable to cool the CCD
chip from 42 to 47 °C below ambient temperature, depending on the
camera type. The Peltier hot side is cooled by a fans. The CCD
chip temperature is regulated with ±0.1 °C precision. High
temperature drop and precision regulation ensure very low dark
current for long exposures and allow proper image calibration.
G4 cameras are available in two variants, differing in
the cooling performance:
Standard cooling cameras achieve regulated
temperature difference up to 42 °C under environment
temperature. Enhanced cooling cameras can regulate
temperature up to 47 °C under environment temperature. Compared
to standard variant, enhanced cooling cameras are somewhat
bulkier due to bigger heat sink, slightly heavier and somewhat
noisier because of more powerful fans.
Comparison of the G4 Mark II standard cooling camera
and enhanced cooling version The camera head contains two temperature sensors — the first sensor measures directly the temperature
of the CCD chip package. The second one measures the temperature
inside the camera shell.
The cooling performance depends on the environmental conditions
and also on the power supply. If the power supply voltage drops
below 12 V, the maximum temperature
drop is lower.
| CCD chip cooling |
Thermoelectric (Peltier modules) |
| Standard cooling ΔT |
45 °C below ambient maximum |
| |
42 °C below ambient typical |
| Enhanced cooling ΔT |
50 °C below ambient maximum |
| |
47 °C below ambient typical |
| Regulation precision |
0.1 °C |
| Hot side cooling |
Air cooling (two fans) |
| |
Optional liquid coolant heat exchanger |
Chip cooling specifications Camera construction does not allow usage of both air and liquid
cooling. Combined cooling (air with the liquid cooling option) is
not available, because such cooling does not work effectively
enough with air only nor with water only.
Power supply
The 12 V DC power supply enables camera operation
from arbitrary power source including batteries, wall adapters
etc. Universal 100-240 V
AC/50-60 Hz, 60 W “brick” adapter is supplied with
the camera. Although the camera power consumption does not
exceed 40 W, the 60 W power supply ensures noise-free
operation.
| Camera power supply |
12 V DC |
| Camera power consumption |
15 W without cooling |
| |
52 W maximum cooling |
| Power plug |
5.5/2.5 mm, center
+ |
| Adapter input voltage |
100-240 V AC/50-60 Hz |
| Adapter output voltage |
12 V DC/5 A |
| Adapter maximum power |
60 W |
Power supply specification Warning: The power connector on the camera head uses
center-plus pin. Although all modern power supplies use this
configuration, always make sure the polarity is correct if
other than the supplied power source is used. 
12 V DC/5 A power supply adapter for G4
camera Mechanical Specifications
Compact and robust camera head measures only 154 × 154 × 65 mm (approx.
6 × 6 × 2.6 inches) for
the model with standard cooling. Enhanced cooling increases camera
depth by 11 mm.
The head is CNC-machined from high-quality aluminum and black
anodized. The head itself contains USB-B (device) connector and
12 V DC
power plug, no other parts (CPU box, USB interface, etc.), except
a “brick” power supply, are necessary. Another connector
allows control of optional external filter wheel. Integrated
mechanical shutter allows streak-free image readout, as well as
automatic dark frame exposures, which are necessary for
unattended, robotic setups.
| Internal mechanical shutter |
Yes, blade shutter |
| Shortest exposure time |
0.2 s |
| Longest exposure time |
Limited by chip saturation only |
| Internal filter wheel |
no |
| Head dimensions |
154 mm × 154 mm × 65 mm
(standard cooling) |
| |
154 mm × 154 mm × 76 mm
(enhanced cooling) |
| Back focal distance |
33.5 mm
(base of adjustable adapters) |
| Standard cooling head weight |
1.6 kg
(without filter wheel) |
| |
2.5 kg
(with “M” external filter wheel) |
| |
2.8 kg
(with “L” external filter wheel) |
| Enhanced cooling head weight |
1.8 kg
(without filter wheel) |
| |
2.7 kg
(with “M” external filter wheel) |
| |
3.0 kg
(with “L” external filter wheel) |
Mechanical specification Camera without filter wheel
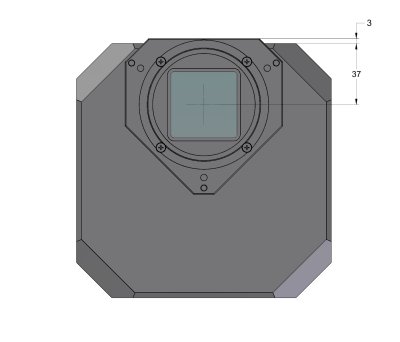
G4 Mark II camera head front view
dimensions G4 Mark II camera head side view
dimensions Enhanced cooling variant
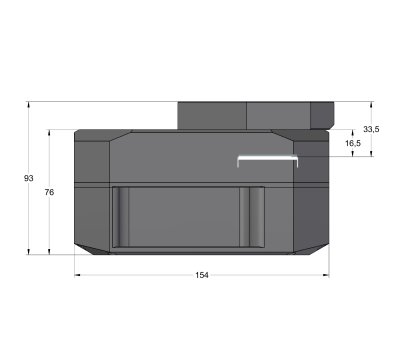
G4 Mark II camera head with Enhanced cooling side
view dimensions Camera with “L” External filter wheel
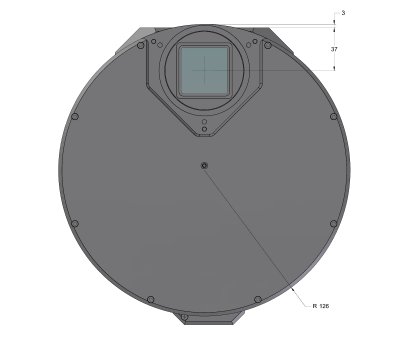
G4 Mark II camera head with External filter wheel
front view dimensions G4 Mark II camera head with External filter wheel
side view dimensions The “M” sized External Filter Wheel diameter is
smaller (see External Filter Wheel User's Guide), but the back
focal distance of all external filter wheels is identical.
Enhanced cooling with External filter wheel
variant
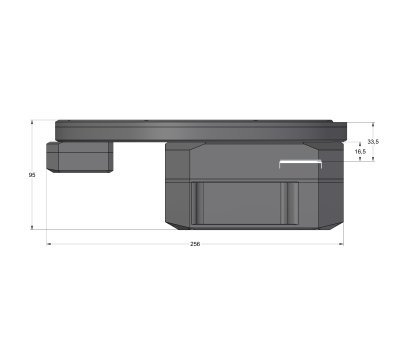
Enhanced cooling G4 Mark II camera head with
External filter wheel side view dimensions Optional accessories
Various accessories are offered with G4 Mark II cameras to
enhance functionality and help camera integration into imaging
setups.
External filter wheels
When there is no filter wheel inside the camera head, all
electronics and firmware, intended to control it, stays idle.
These components can be utilized to control external filter
wheel with only little changes. Also the camera front shell
can be manufactured thinner, the space for filter wheel is
superfluous.

G4 Camera Mark II without filter wheel (left), with
“M” size (center) and “L” size (right)
External filter wheels Telescope adapters
Usage of many common types of telescope and lens
adapters are ruled out by very large sensor used in G4 Mark
II cameras. The CCD diagonal dimension of G4 cameras is
52 mm, which is greater than
outer dimensions of many adapter kinds. Only the M68
threaded and Canon EOS bayonet adapters are large enough not
to cause vignetting.
M68 × 1 — adapter
with M68 × 1 inner thread and
47.5 mm back
focal distance. Canon EOS bayonet — standard Canon EOS lens adapter, preserves
44 mm back focal
distance.
All telescope/lens adapters of the G4 Mark II series of
cameras can be slightly tilted. This feature is introduced to
compensate for possible misalignments in perpendicularity of
the telescope optical axis and sensor plane.
The Mark II camera telescope adapters are attached using
three “pulling” screws. As the adapter tilt is
adjustable, another three “pushing” screws are intended
to fix the adapter after some pulling screw is released to
adjust the tilt.
Adjusting the telescope adapter tilt (left) and
removing tiltable the adapter (right) Adjustable telescope/lens adapters are attached
slightly differently depending if the adapter is attached
directly to the camera head (e.g. when camera is equipped
with internal filter wheel) or to the External filter wheel
case.
G4 Mark II adapters are not mounted directly on the
camera head. Instead a tilting adapter base, holding the
circular spring, is always used. If the External filter wheel is used, the adapted
base is not necessary, as the Mark II External filter wheel
front plate is already designed to hold the spring and it
also contains threads to fix respective adapters.

Mark II External filter wheels are already designed
to for adjustable telescope adapters Off-Axis Guider adapter
G4 camera can be optionally equipped with Off-Axis Guider
Adapter. This adapter contains flat mirror, tilted by 45° to
the optical axis. This mirror reflects part of the incoming
light into guider camera port. The mirror is located far
enough from the optical axis not to block light coming to the
main camera sensor, so the optics must be capable to create
large enough field of view to illuminate the tilted
mirror.
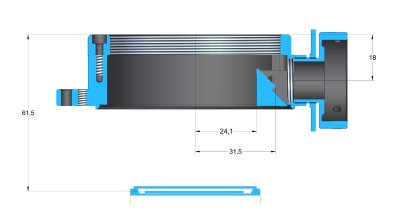
Position of the OAG reflection mirror relative to
optical axis The G4-OAG offers the M68 × 1
thread on the telescope side. The back focal distance is
61.5 mm.
If the OAG is used on camera without filter wheel, thicker
adapter base must be used to keep the Back focal distance and
to allow the guiding camera to reach focus.
G4 OAG adapter (left), OAG on G4 camera with thick
adapter base (right) OAG guider port is compatible with G0 and G1 cameras. It is
necessary to replace the CS/1.25” adapter with short, 10 mm
variant in the case of G1 cameras. Because G1 cameras follow
CS-mount standard, (BFD 12.5 mm), any camera following this
standard with 10 mm long 1.25” adapter should work properly
with the G4-OAG.
Attaching camera head to telescope mount
G4 Mark II cameras are equipped with two “tripod”
0.250-20UNC threads on the top side of the camera head. This
thread can be used to attach 1.75 inch “dovetail bar”
(Vixen standard). It is then possible to attach the camera
head, e.g. equipped with photographic lens, directly to
various telescope mounts supporting this standard.

1.75" bar for standard telescope mounts Spare desiccant containers
The G4 Mark II cameras are supplied with silica-gel
container, intended to dry the CCD cold chamber. This
container can be unscrewed and desiccant inside can be dried
in the owen (see the camera User's Manual).

The whole desiccant container can be baked to dry
the silica-gel inside or its content can be poured out after
unscrewing the perforated internal cap and baked
separately Container shipped with the camera by default does not
exceed the camera head outline. It is equipped with a slot for
tool (of for just a coin), allowing releasing and also
tightening of the container. Containers intended for enhanced
cooling cameras are prolonged as the camera thickness is
greater in the case of this variant.

Containers for standard and enhanced cooling
cameras also in variants allowing tool-less
manipulation It is possible to order spare container, which makes
desiccant replacement easier and faster. It is possible to dry
the spare container with silicagel and then only to replace it
on the camera. Spare container is supplied including the
air-tight cap.
Spare container can be supplied also in a variant that
allows manipulation without tools. But this container is
longer and exceeds camera outline. If the space behind the
camera is not critical, this container can make desiccant
exchange even easier.

Silicagel container with slot (left) and variant
for tool-less manipulation (right) Camera head color variants
Camera head is available in several color variants of the
center plate. Visit manufacturer's web pages for current
offering.

G4 Mark II camera color variants Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter
Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter allows connection of up to 4 Gx
cameras of any type on the one side and 1 Gbps Ethernet on the
other side. This adapter allows access to connected Gx cameras
using routable TCP/IP protocol over practically unlimited
distance.
The Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter device (left) and
adapter with two connected cameras (right) Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter devices are described in detail
here.
Software Support
Powerful SIPS (Scientific Image Processing System)
software, supplied with the camera, allows complete camera control
(exposures, cooling, filter selection etc.). Also automatic
sequences of images with different filters, different binning etc.
are supported. With full ASCOM standard support, SIPS can be also
used to control other observatory equipment. Specifically the
telescope mounts, but also other devices (focusers, dome or roof
controllers, GPS receivers etc.).
SIPS also supports automatic guiding, including image
dithering. Both “autoguider” port hardware interface
(6-wire cable) and mount “Pulse-Guide API” guiding methods
are supported. For hi-quality mounts, capable to track without the
necessity to guide at last during one exposure, inter-image
guiding using the main camera only is available.
SIPS controlling whole observatory (shown in optional
dark skin) But SIPS is capable to do much more than just camera and
observatory control. Many tools for image calibration, 16 and
32 bit FITS file handling, image set
processing (e.g. median combine), image transformation, image
export etc. are available.
SIPS handles FITS files, supports image calibration and
processing As the first “S” in the abbreviation SIPS means
Scientific, the software supports astrometric image reduction as
well as photometric processing of image series.
SIPS focuses to advanced astrometric and photometric
image reduction, but also provides some very basic
astro-photography processing SIPS software package is freely available for download from this www site. All functions are
thoroughly described in the SIPS User's Manual, installed with
every copy of the software.
Drivers for ASCOM standard as well as native drivers for
third-party software are also available (e.g. TheSkyX, MaxIm DL,
AstroArt, etc.). Visit the download page of this web site for current list
of available drivers, please.
Also INDI drivers for 32 bit and
64 bit Linux running on x86 and ARM
are available. Also drivers for TheSkyX package running on macOS
are supplied with the camera.
Automatic guiding
SIPS software package allows automatic guiding of the
astronomical telescope mounts using separate guiding camera.
Proper and reliable automatic guiding utilizing the
computational power of Personal Computer (e.g. calculation of
star centroid allows guiding with sub-pixel precision) is not
simple task. Guiding complexity corresponds to number of
parameters, which must be entered (or automatically
measured).
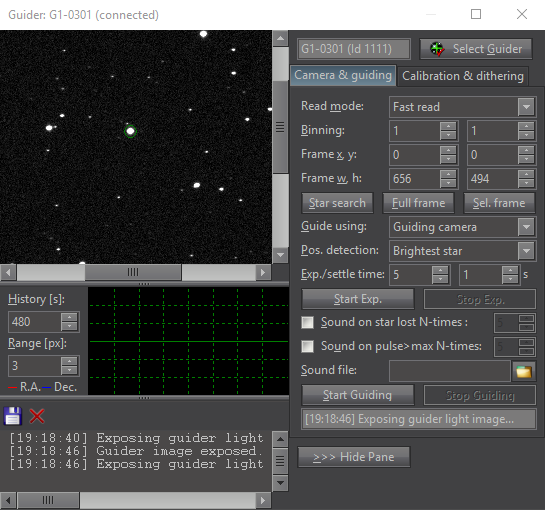
The SIPS “Guider” tool window The “Guiding” tool allows switching of autoguiding
on and off, starting of the automatic calibration procedure
and recalculation of autoguiding parameters when the telescope
changes declination without the necessity of new calibration.
Also swapping of the German Equatorial mount no longer
requires new autoguider calibration. There is also a graph
showing time history of guide star offsets from reference
position in both axes. The length of graph history as well as
the graph range can be freely defined, so the graph can be
adjusted according to particular mount errors and periodic
error period length. Complete log of calibration procedure,
detected offsets, correction pulses etc. is also shown in this
tool. The log can by anytime saved to log file.
An alternative to classic autoguiding is the inter-image
guiding, designed for modern mounts, which are precise enough
to keep tracking with sub-pixel precision through the single
exposure, and irregularities only appear on the
multiple-exposure time-span. Inter-image guiding then performs
slight mount position fixes between individual exposures of
the main camera, which eliminates “traveling” of the
observed objects through the detector area during observing
session. This guiding method uses main imaging camera, it does
not use another guiding camera and naturally does not need
neither OAG nor separate guiding telescope to feed the light
into it.
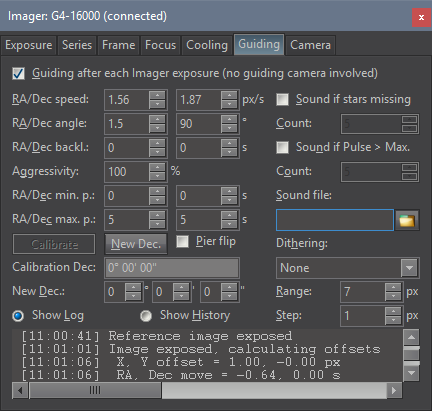
Inter-image guiding controls in the
Guiding tab of the Imager Camera tool
window Shipping and Packaging
G4 Mark II cameras are supplied in the foam-filled,
hard carrying case containing:
Camera body with a user-chosen telescope adapter. If
ordered, the filter wheel is already mounted inside the camera
head and filters are threaded into place (if ordered). A 100-240 V AC input, 12 V DC output
“brick” adapter with 1.8 m
long power cable. 5 m long USB A-B cable for
connecting camera to host PC. USB Flash Drive with camera drivers, SIPS software
package with electronic documentation and PDF version of
User's Manual. A printed copy of camera User's Manual
G4 cameras are shipped in the foam-filled carrying case
(left), larger case is used if camera is ordered with external
filter wheel (right) Image Gallery
Example images captured with G4 cameras.
 |
| Object |
M16 “Eagle Nebula” |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
0.5 m CDK |
| Exposure |
44.25 hours |
|  |
| Object |
M16 “Eagle Nebula” |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
HOORGB |
| Telescope |
0.5 m CDK |
| Exposure |
5.25 hours (RGB) |
|
 |
| Object |
SH2-308 planetary nebula |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGBHαOIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
89 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC5128 “Centaurus A” galaxy |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
LRGBHα |
| Telescope |
CDK 20" f/6.8 (500mm/3400mm) |
| Exposure |
42.24 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
surroundings of the star ρ
Ophiuchi |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
67.5 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M83 “Southern Pinwheel” galaxy |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGBHα |
| Telescope |
CDK 20" f/6.8 (500mm/3400mm) |
| Exposure |
25 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M8 “Lagoon” |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
104 hours |
|  |
| Object |
M8 “Lagoon” |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
5 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6357 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
108 hours |
|  |
| Object |
NGC6357 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
10 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6334 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
72 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC3586 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
103 hours |
|  |
| Object |
NGC3586 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
4 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M51 “Whirlpool” galaxy |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGBHα |
| Telescope |
CDK 20" f/6.8 (500mm/3400mm) |
| Exposure |
25 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6188 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
108 hours |
|  |
| Object |
NGC6188 |
| Author |
J. C. Canonne, N. Outters, P. Bernhard, D.
Chaplain, L. Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
TEC160 |
| Exposure |
7 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
IC443 “Jellyfish” nebula (mosaic) |
| Author |
J.C. Canonne, P. Bernhard, D. Chaplain & L.
Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
FSQ106, TEC140, AP155, RH200 |
| Exposure |
113 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
“Veil” nebula (mosaic) |
| Author |
J.C. Canonne, P. Bernhard, D. Chaplain & L.
Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 and AP155 |
| Exposure |
415 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
IC2944 |
| Author |
J.C. Canonne, P. Bernhard, D. Chaplain & L.
Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC160 f/7 |
| Exposure |
101 hours |
|  |
| Object |
IC2944 |
| Author |
J.C. Canonne, P. Bernhard, D. Chaplain & L.
Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
TEC160 f/7 |
| Exposure |
5.25 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC7635 “Bubble” nebula, M52 cluster |
| Author |
J.C. Canonne, P. Bernhard, D. Chaplain & L.
Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC140 |
| Exposure |
88 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M106 galaxy |
| Author |
Michael Miller, Warren Keller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
Astrodon LRGB |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC2264 “Christmas Tree” nebula |
| Author |
Reinhard Wallner |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
HαRGB |
| Telescope |
TEC 160FL |
| Exposure |
13 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
Dentelles-2 nebula |
| Author |
Nicolas Outters |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
SII Hα OIII |
| Telescope |
Newton SV400 F3.8 |
| Exposure |
37 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
IC1396 “Elephhant Trunk” nebula |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas, processed by Martin Myslivec |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
30cm f/4 Newtonian |
| Exposure |
10 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M31 “Great Andromeda Galaxy” |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas, processed by Martin Myslivec |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
30cm f/4 Newtonian |
| Exposure |
1.5 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M42 “Great Orion Nebula” |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas, processed by Martin Myslivec |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
30cm f/4 Newtonian |
| Exposure |
1 hour |
|
 |
| Object |
M45 “Pleiades” |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas, processed by Martin Myslivec |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
30cm f/4 Newtonian |
| Exposure |
1.5 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
“Flame” and “Horse Head” nebulae in
Orion |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
30cm f/4 Newtonian |
| Exposure |
1 hour |
|
 |
| Object |
IC1396 “Elephant trunk” nebulosity
complex |
| Author |
J.C. Canonne, P. Bernhard, D. Chaplain & L.
Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
AP155 |
| Exposure |
73 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
Sh2-129 “Bat” and OU4 “Squid”
nebulae |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
TEC140 APO + Takahashi CCA 250 |
| Exposure |
127 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M27 “Dumbbell” planetary nebula |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB + narrow-band Hα,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Takahashi CCA 250 mm
f/5 |
|
 |
| Object |
IC5067 nebula |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Officina Stellare UCRC 300 |
|
 |
| Object |
M31 Big Andromeda Galaxy |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB |
| Telescope |
Takahashi CCA 250 mm
f/5 |
|
 |
| Object |
M33 galaxy in Triangulum |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
RGB + narrow-band Hα |
| Telescope |
Takahashi CCA 250 mm
f/5 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC2244 “Rosette” nebula |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Officina Stellare UCRC 300 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6888 “Crescent” nebula |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII |
| Telescope |
Officina Stellare UCRC 300 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC7635 “Bubble” nebula |
| Author |
Frédéric Lambert |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Takahashi CCA 250 mm
f/5 |
|
 |
| Object |
IC1805 nebula |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Orion Optics/Skymeca 50 cm MDK f/6,8 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC7635 “Bubble Nebula” in Cassiopeia |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Orion Optics/Skymeca 50 cm MDK f/6,8 |
|
 |
| Object |
IC63 nebula in Cassiopeia |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
LRGB |
| Telescope |
Orion Optics/Skymeca 50 cm MDK f/6,8 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC7380 “Wizadr Nebula” in Cepheus |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
Orion Optics/Skymeca 50 cm MDK f/6,8 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC7822 star forming region in Cepheus |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII |
| Telescope |
FSQ106ed |
|
 |
| Object |
“North America” and “Pelican”
nebulae |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon and Didier Chaplain |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII,
OIII a NII |
| Telescope |
FSQ106ed |
| Exposure |
65 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
M31 galaxy in Andromeda |
| Author |
Philippe Bernhard |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
LRGB |
| Telescope |
RH200 |
| Exposure |
3 hours |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6960 “Veil” nebula |
| Author |
Laurent Bourgon |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII a
OIII |
| Telescope |
Orion Optics/Skymeca 50 cm MDK f/6,8 |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC7000 mlhovina “Severní Amerika” |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
narrow-band Hα, SII a
OIII |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6960 “Veil” nebula |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
Astrodon LRGB |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
NGC6992 “Veil nebula” |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
Astrodon LRGB |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
M51 “Whirlpool” galaxy |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
Astrodon LRGB |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
M16 “Eagle” nebula |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
Astrodon LRGB |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
M16 “Eagle” nebula |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
H-alpha, OIII and SOII narrow-band |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
| Object |
M63 “Sunflower” galaxy |
| Author |
Michael Miller |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW-L-7 |
| Filters |
Astrodon LRGB |
| Telescope |
152mm APM APO |
|
 |
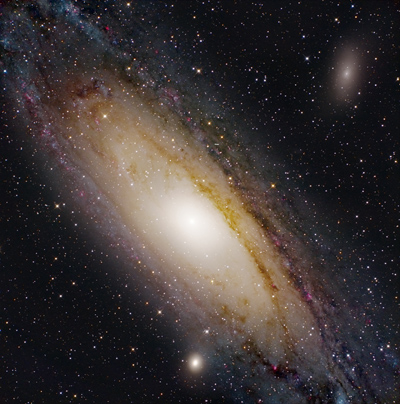
| Object |
“North America” and “Pelican”
nebulae |
| Author |
Petr Novak |
| Camera |
G4-16000 + EFW4-5 |
| Filters |
12nm H-alfa |
| Telescope |
Takahashi FSQ 106 ED |
|
 |
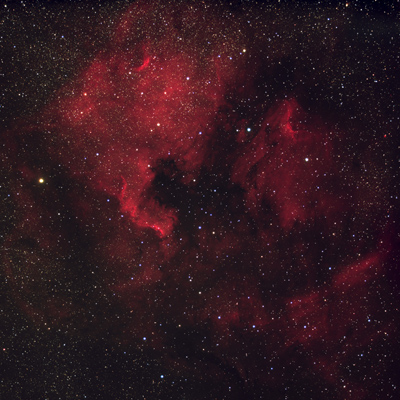
| Object |
M31 Great Andromeda Galaxy |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas, processed by Martin Myslivec |
| Camera |
G4-16000 (cropped to 3k × 3k pixels) |
| Filters |
Astronomik LHaRGB |
| Telescope |
Orion SPX 250 + Paracorr |
|
 |
| Object |
“North America” and “Pelican”
nebulae |
| Author |
Martin Myslivec |
| Camera |
G4-16000 |
| Telescope |
Borg 66 ED |
|
 |
| Object |
Field of variable star V729 Aql |
| Author |
Pavel Cagas, field composition Vaclav Pribik |
| Camera |
G4-16000 (cropped to 3k × 3k pixels) |
| Filters |
Clear |
| Telescope |
Orion SPX 250 + Paracorr |
|
All images published with permission of their respective
authors.
|
